By submitting your email you agree to receive information about relevant products and services. You may unsubscribe at any time. Read our Privacy Policy here.
A control plan describes the methods for controlling product and process variation in order to produce quality parts that meet customer requirements.
Control plans are a critical part of the overall quality process. They are living documents that are updated as processes change and improve throughout the product lifecycle. Control plans are also one of the requirements of the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP).
Control plans may vary depending on customer requirements, but should include information about product and process characteristics that must be controlled, as well as the control methods for those characteristics. They should also include the relevant revision and approval dates, contact information, and references to other quality documents when appropriate.
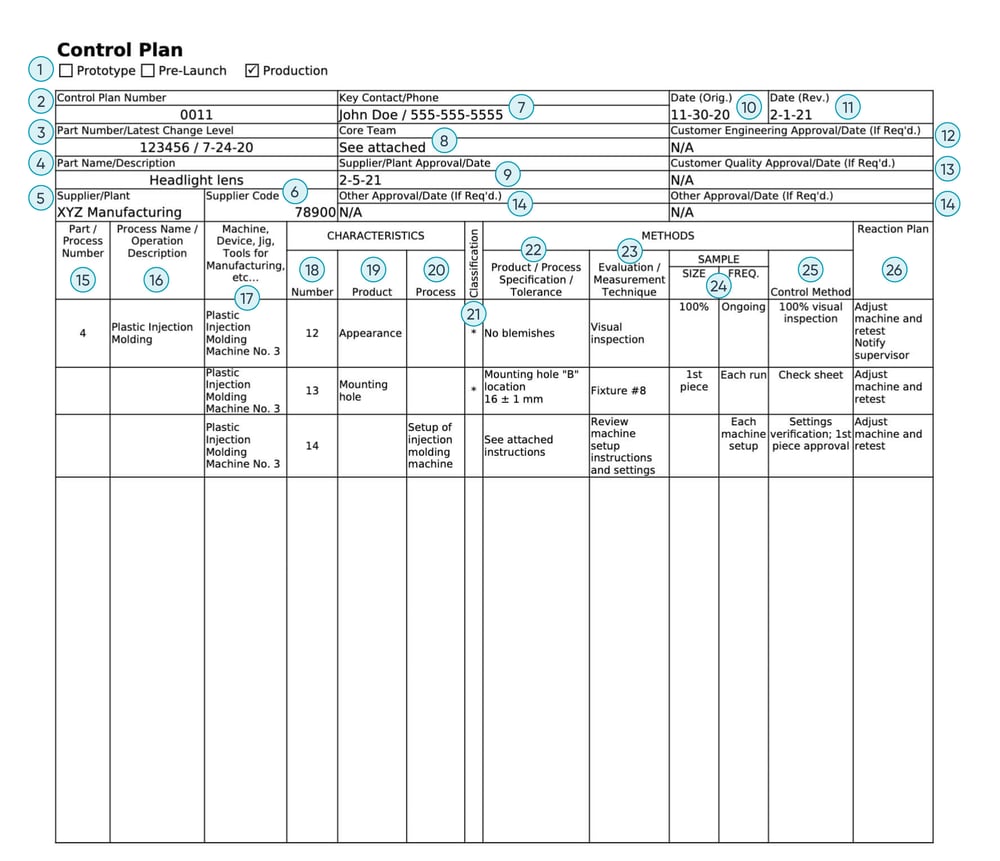
1. Prototype, Pre-Launch, or Production
Choose the appropriate category based on the manufacturing stage.
2. Control Plan Number
The control plan document number (if applicable).
3. Part Number/Latest Change Level
The number of the system or component being controlled, and the latest change level or issue date.
4. Part Name/Description
The name and description of the part or process being controlled.
5. Supplier/Plant
The name of the company and the division, department, or plant preparing the control plan.
6. Supplier Code
Identification number or customer supplier code.
7. Key Contact/Phone
Name and contact info for the primary person responsible for the control plan.
8. Core Team
Name and contact info for all team members responsible for preparing the control plan (can be attached separately).
9. Supplier/Plant Approval/Date
The responsible manufacturing plant approval.
10. Date (Orig.)
The date the original control plan was created.
11. Date (Rev.)
The date of the most recent control plan revision.
12. Customer Engineering Approval/Date
The responsible customer engineering approval, if required.
13. Customer Quality Approval/Date
The responsible customer quality representative approval, if required.
14. Other Approval/Date
Any other approvals required.
15. Part/Process Number
The part number or numbers, typically found in the Process Flow Chart.
16. Process Name/Operation Description
The process or operation name from the flow diagram that describes the steps for manufacturing the system or component.
17. Machine, Device, Jig, Tools for Manufacturing, etc.
The processing equipment or manufacturing tools used in the operation.
Characteristics (#18-20)
The special properties or features of a product or process. Reference or attach relevant documents and visual aids where applicable.
18. Number
The cross reference number for all relevant documents. For example, this would be the same number across ballooned part drawings, process flow diagrams, FMEAs, or other documents.
19. Product
All special characteristics or features of a part, component, or assembly, compiled from drawings or other sources. This section can also include other features that typically involve process control tracking.
20. Process
The process or input variables that must be controlled to decrease product variation. There can be one or more process characteristics that affect each listed product characteristic.
21. Classification
The special characteristic classification if required (symbols used by the customer to mark important features), or leave blank for other undesignated features.
Methods (#22-25)
The plan or system (including procedures, tools, etc) for controlling the products and processes.
22. Product/Process Specification/Tolerance
Specifications and tolerances from relevant engineering documents (including drawings, design reviews, etc).
23. Evaluation/Measurement Technique
The measurement system used for each part, feature, process, or manufacturing equipment (for example, gages, tools, test equipment, etc). This should be regularly evaluated using a measurement systems analysis.
24. Sample: Size/Freq.
The corresponding sample size and frequency when sampling is required.
25. Control Method
Description of how the operation will be controlled, based on the strategy and analysis of the manufacturing process, the type of process, and risks found during quality planning. This is a key part of the control plan and should be regularly evaluated. Control methods can include inspection, statistical process control, sampling plans, and others.
26. Reaction Plan
The specific corrective actions for avoiding production of nonconforming products. This section can reference a separate reaction plan if needed and assign the responsible team members.
What's included:
What’s included:
Copyright 2025 InspectionXpert Corporation, is a wholly owned subsidiary of Ideagen Inc, All Rights Reserved